|
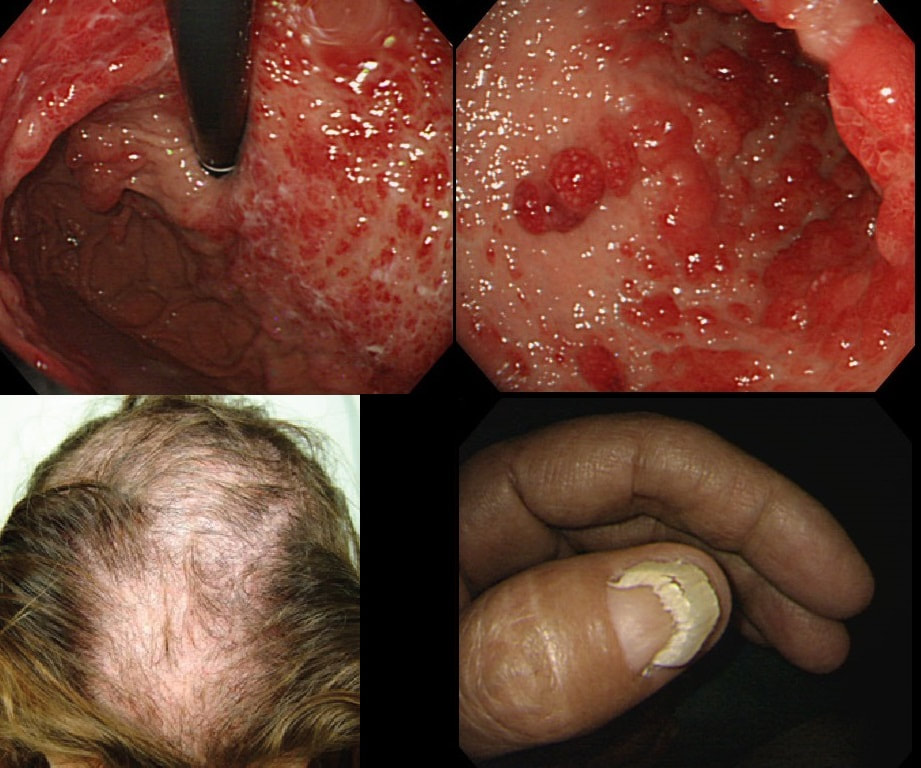
You are called into another endoscopy room to give an opinion on this gastric findings. It's a 65 year old man undergoing investigations for severe weight loss and anaemia. The anaemia was discovered by the dermatologists where he had been referred for investigations of suspected onychogryphosis and thinning of the hair.
WHAT IS THE EXPLANATION FOR THE GASTRIC POLYPS?
■ Likely hyperplastic polyps
INCORRECT!
■ Likely hamartomatous polyps
CORRECT! Clearly you know what the underlying diagnosis is?
■ Likely florid GAVE
INCORRECT!
■ Likely lymphoma
Gastric Lymphomas are usually ulcerated
■ Likely linitis plastica
INCORRECT! (although I guess it could be)
explanation
The nail dystrophy is not due fungal infection (onychogryphosis). In fact, this patient has Cronkhite-Canada syndrome. This enigmatic acquired syndrome is characterised by malabsorption, gastrointestinal polyposis, nail dystrophy, alopecia, cutaneous pigmentation, diarrhoea and weight loss. The nail dystrophy and skin pigmentation is clearly seen in the photograph. Other common symptoms include abdominal discomfort and a protein loosing enteropathy. The underlying cause is unknown. The cutaneous manifestations are probably all secondary to severe malnutrition due to diffuse small bowel mucosal involvement.
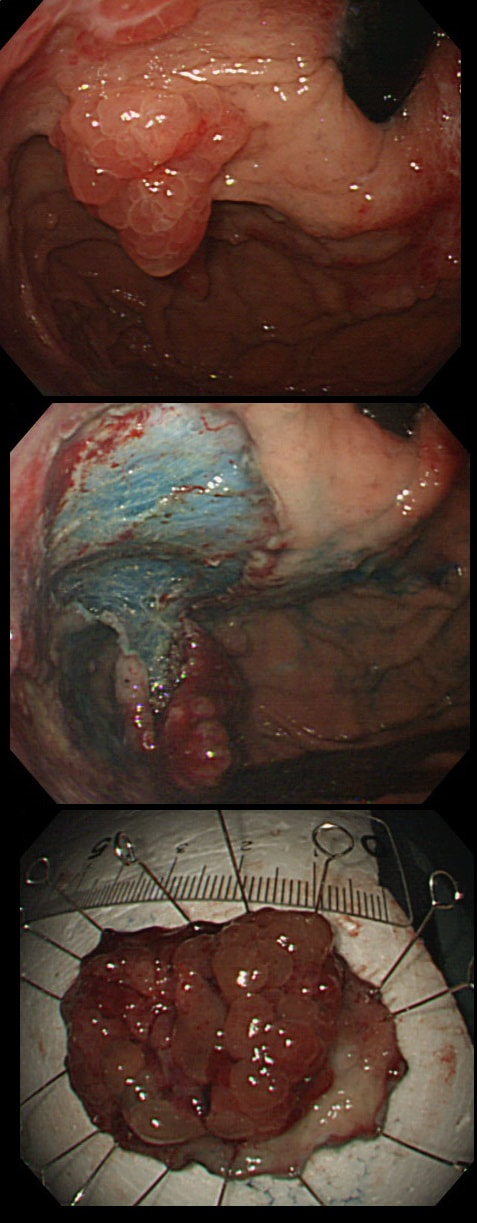
Histologically the mucosa is oedematous with dilated glands and an inflammatory cell infiltrate of the lamina propria. Gastrointestinal polyps are hamartomatous but may contain foci of adenomatous epithelium. The histopathologists will struggle in interpreting the biopsy findings and will mention things like 'marked foveolar hyperplasia', 'cystically dilated irregular glands', 'oedematous stroma' and 'scattered mixed inflammatory cells'. The differential diagnosis of such hamartomatous findings includes juvenile polyposis syndrome, Cronkhite-Canada syndrome, hyperplastic polyposis and Menetrier's disease. Of course, it will help them to know about the nails and hairloss etc!!! Malignant transformation has been reported and may not be as rare as initially thought . The prognosis is said to be poor but I'm not sure that this is still the case with 'modern management'. Interestingly, in this case a suspicious nodule was found (image below). It was removed endoscopically and found to be an early gastric cancer! |
Categories
All
|